10 Mysterious Places Where Water Vanishes Without a Trace
6. Lake Beloye: The Vanishing Lake of Russia
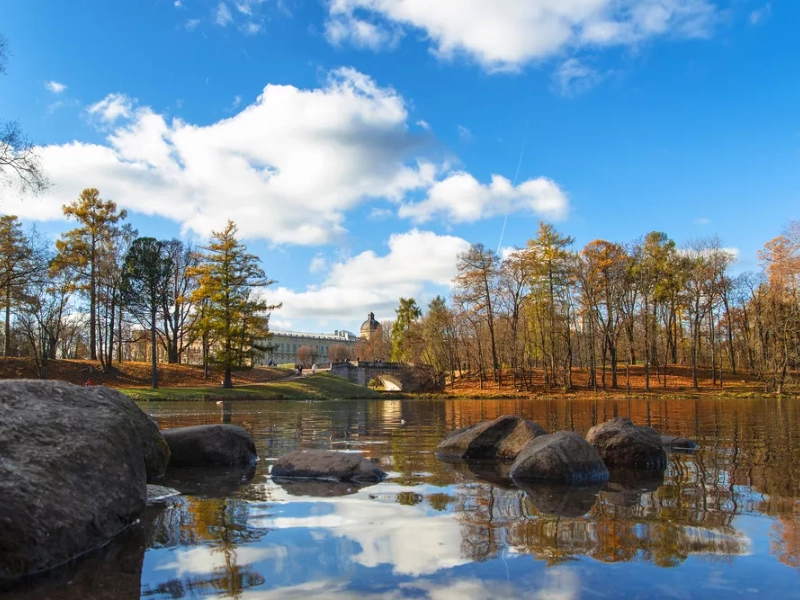

Geologists and hydrologists quickly began investigating the phenomenon, seeking to identify the mechanisms responsible for such rapid and complete lake drainage. Their research revealed that the area's specific geological composition played a crucial role in this extraordinary event. The region around Lake Beloye is characterized by karst topography, a landscape formed by the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum.
Karst topography is distinguished by features such as sinkholes, caves, and underground drainage systems. In Lake Beloye's case, it appears that the lake's water found a pathway into this underground network, likely through a collapse or opening in the overlying rock layers. This connection to the subterranean system essentially transformed the lake into a massive sinkhole, where its waters could rapidly drain into the ground below.
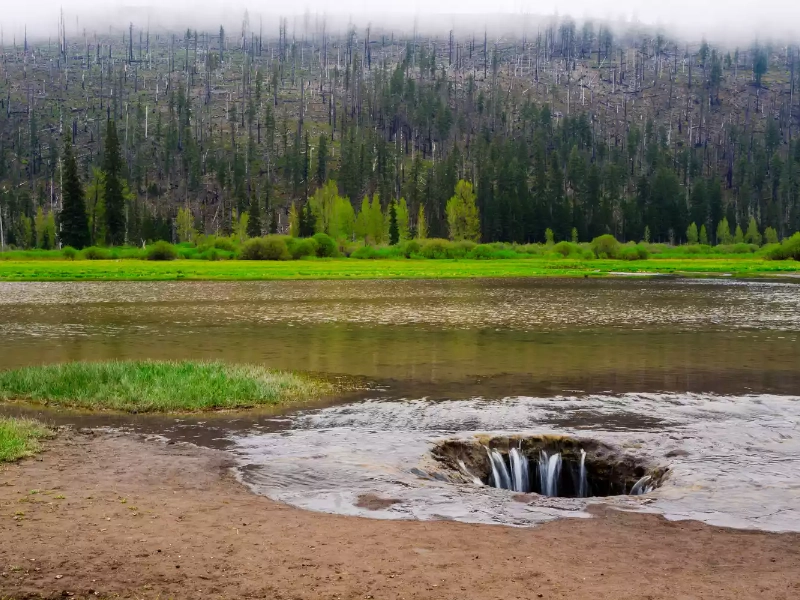
Further evidence of this karst-related drainage came from the discovery of the large crater and hole at the bottom of the empty lake bed. This opening is believed to be the primary pathway through which the lake's water escaped, connecting the surface water to the extensive system of underground channels and caverns characteristic of karst environments.
Intriguingly, Lake Beloye's story did not end with its initial disappearance. Over a year after the catastrophic drainage event, observers reported that the former cavity began filling with water again. This refilling process offered hope that the lake might return to its natural state. However, in a twist that further complicated the local hydrology, the newly accumulated water quickly disappeared again, leaving the basin empty once more.
This cycle of filling and draining emphasizes the dynamic and complex nature of karst hydrology. The underground processes that initially caused the lake to vanish likely continue to influence the lake's behavior, creating a balance between surface water accumulation and underground drainage.
While the exact underground path of the lake's water remains unknown, scientists believe most of it probably ended up in the nearby Oka River. This theory is consistent with our understanding of how water typically moves through karst systems, often emerging in springs or joining existing water bodies some distance from where it entered the ground.
The case of Lake Beloye provides a dramatic illustration of the hidden complexity that exists beneath Earth's surface. It emphasizes the importance of understanding local geology when assessing environmental stability and predicting potential natural hazards. The sudden disappearance of a lake is not merely a curiosity; it can have significant implications for local ecosystems, water supplies, and human populations that depend on these water bodies.
The Lake Beloye incident also highlights the importance of continued monitoring and research in areas with karst terrain. As climate change and human activities continue to affect geological and hydrological systems worldwide, events like Lake Beloye's disappearance may become more frequent or unpredictable. Understanding these processes is crucial for effective land use planning, water resource management, and environmental conservation efforts.
The story of Lake Beloye remains a source of fascination for both locals and scientists, serving as a reminder of the dynamic and sometimes unpredictable nature of our planet's geological processes. Each new discovery about this vanishing lake contributes to our understanding of karst environments and the complex interactions between surface and groundwater systems.